Emergency Care for Oral Soft Tissue Injuries: What You Need to Know
Oral soft tissue injuries refer to wounds or damage to the mucous membranes, tongue, lips, cheeks, and gums inside the mouth. These injuries can be caused by various factors, including trauma, accidents, sports, or even minor incidents like biting the tongue or cheek. If you suffer or experience any injury consult the dentist in Middle Village, Queens, NY for further assessment and treatment.
What are the types of oral soft tissue injuries?
Here are some common types of oral soft tissue injuries:
Lacerations
– Cuts or tears in the mucous membranes, tongue, lips, or cheeks
– Can be shallow or deep, and may require suturing
Contusions
– Bruises or swelling in the soft tissues
– Can be painful and may take time to heal
Abrasions
– Scrapes or rubs on the mucous membranes or gums
– Can be painful and may bleed
Avulsions
– Tears or pulling away of soft tissue from the underlying bone or teeth
– Can be severe and require immediate attention
Burns
– Thermal or chemical burns to the oral soft tissues
– Can be painful and may require specialized treatment
Hematomas
– Blood accumulation in the soft tissues
– Can be painful and may require drainage
Ulcers
– Open sores or lesions on the mucous membranes or tongue
– Can be painful and may take time to heal
Fractures
– Breaks in the jawbone or facial bones
– Can be severe and require immediate attention
Soft tissue trauma
– Injuries to the lips, cheeks, or tongue
– Can be painful and may require suturing
Mucosal tears
– Tears in the mucous membranes
– Can be painful and may bleed
What causes oral soft tissue injuries?
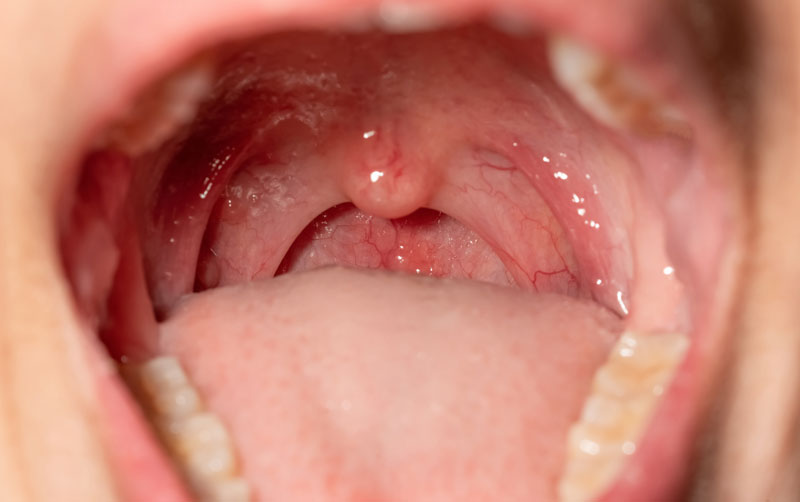
Oral soft tissue injuries can be caused by various factors, including:
Trauma
– Falls
– Accidents
– Physical abuse
– Sports injuries
Biting or chewing
– Accidental biting of the tongue, cheek, or lip
– Chewing hard objects like ice, nuts, or hard candy
Thermal or chemical burns
– Drinking hot liquids
– Eating spicy or acidic foods
– Exposure to chemicals like bleach or acid
Sports and recreational activities
– Contact sports like hockey, football, or basketball
– Skateboarding or cycling accidents
Orthodontic appliances
– Broken brackets or wires
– Irritation from orthodontic devices
Dental procedures
– Complications from dental surgery
– Accidental damage during dental treatment
Systemic diseases
– Diabetes
– Autoimmune disorders
– Nutritional deficiencies
Infections
– Bacterial or viral infections
– Fungal infections like thrush
Medications
– Side effects from certain medications
– Overuse of certain medications
Other factors
– Aging
– Poor oral hygiene
– Smoking or tobacco use
What are the symptoms of oral soft tissue injuries?
Symptoms of oral soft tissue injury may include:
- Pain or tenderness
- Swelling or bruising
- Bleeding or oozing
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Changes in sensation or numbness
- Redness or inflammation
- Ulcers or sores
- Crusting or scabbing
- Foul taste or bad breath
- Difficulty moving the tongue or jaw
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Chewing or biting difficulties
- Soreness or discomfort
- Visible wounds or cuts
How are oral soft tissue injuries treated?
Here are some common treatment options:
First aid
– Stop bleeding with pressure or ice
– Clean the wound with saltwater or antibacterial mouthwash
– Apply topical anesthetics like Orajel or Anbesol
Dental evaluation
– Assess the extent of the injury
– Check for signs of infection or nerve damage
Suturing
– Close lacerations or avulsions with stitches
– Promote healing and prevent scarring
Pain management
– Prescribe pain medication like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
– Use topical anesthetics or numbing gels
Antibiotics
– Prevent or treat infections
– Use broad-spectrum antibiotics like amoxicillin or penicillin
Wound care
– Clean and dress the wound regularly
– Apply topical antibiotics or creams
Surgical interventions
– Repair damaged tissues or bone
– Reattach avulsed teeth or tissue
Laser treatment
– Promote healing and reduce pain
– Use low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
Oral soft tissue injuries can be painful and potentially serious. Prompt treatment and proper care are essential to prevent complications and promote healing. By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage oral soft tissue injuries, maintaining optimal oral health and overall well-being.